「Table-related commands in STATA」の版間の差分
ナビゲーションに移動
検索に移動
Vaccipedia.admin (トーク | 投稿記録) |
Vaccipedia.admin (トーク | 投稿記録) |
||
| 188行目: | 188行目: | ||
==Two-way, multiple== | ==Two-way, multiple== | ||
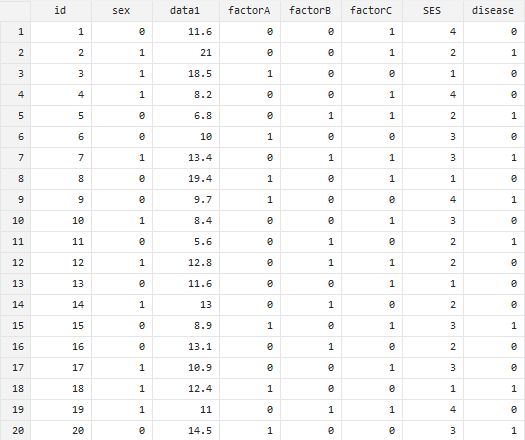
===Summary of ''factorA'', ''factorB'', ''factorC'' based on ''disease''=== | ===Summary of ''factorA'', ''factorB'', ''factorC'' based on ''disease''=== | ||
| + | {|class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !rowspan="3"|tabstat | ||
| + | |[[File:tabstat_factorABC_by(disease).jpg]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
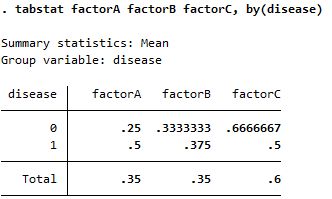
| + | |[[File:tabstat_factorABC_by(disease)_statistic(sum).jpg]] | ||
| + | |factorA,B,C are binary variables so summations of values provide the positivities of factorA,B,C | ||
| + | |- | ||
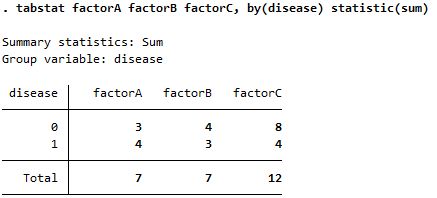
| + | |[[File:tabstat_factorABC_by(disease)_statistic(n).jpg]] | ||
| + | |''statistic(n)'' (''statistic(count)'' is the same) only counts observations with real values, which only tell non-missing observations | ||
| + | |} | ||
2023年4月2日 (日) 18:15時点における版
目次
Abbreviations of commands
| table | (no abbv.) |
|---|---|
| tabulate | ta tab |
| tabstat | (no abbv.) |
| summarize | su |
Differences between table, tabulate, tabstat, summarize
| one-way | two-way | options | |
|---|---|---|---|
| table | table v1 create a one-way table |
table v1 v2 create a two-way table |
,statistics( ) |
| tabulate | tabulate v1 create a one-way table |
tabulate v1 v2 create a two-way table |
,chi2 Pearson's chi-squared test; *only for two-way ,summarize(v3) detailed statistics for v3 |
| tabstat | tabstat v1 create a one-way table of v1 |
*no two- or multiple-way table | ,statistics( ) ,by(v3) detailed statistics for each of v3 |
| summarize | summarize v1 detailed statistics of v1 |
*no two- or multiple-way summary | ,detail |
† row = transverse direction, column = longitudinal direction
Sample data
Suppose we have such a dataset in STATA.
One-way
Summary of sex, a binary variable
| table | 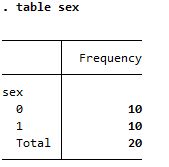
|
Both reports frequency but tabulate is more detailed |
|---|---|---|
| tabulate | 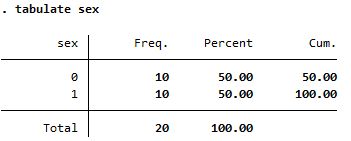
| |
| tabstat | 
|
Both reports mean but summarize is more detailed |
| summarize | 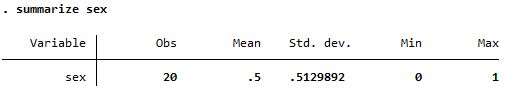
|
Summary of data1, a continuous variable
| table | 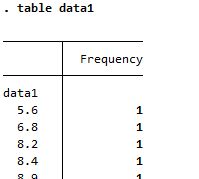
|
Both reports frequency of each value, which does not make sense |
|---|---|---|
| tabulate | 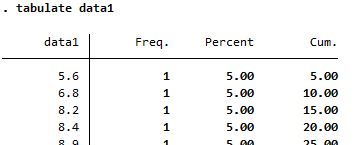
| |
| tabstat | 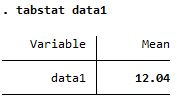
|
Both reports mean but summarize is more detailed |
| summarize | 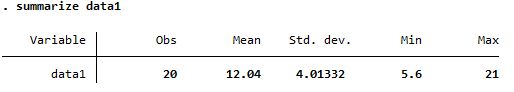
|
Summary of SES, a categorical variable
| table | 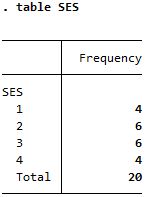
|
Both reports frequency but tabulate is more detailed |
|---|---|---|
| tabulate | 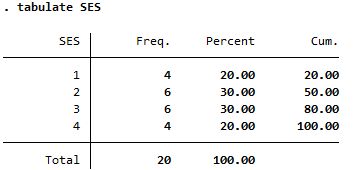
| |
| tabstat | 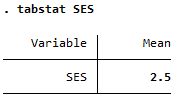
|
Both reports mean but summarize is more detailed |
| summarize | 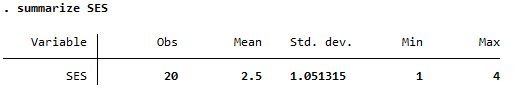
|
One-way, multiple
| table | *Both do not create one-way multiple table | |
|---|---|---|
| tabulate | ||
| tabstat | 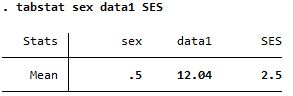
|
Reports mean in row (transverse) direction |
| summarize | 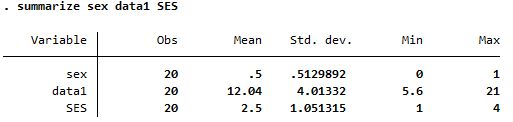
|
Reports more details in column (longitudinal) direction |
Two-way
Summary of factorA based on sex
| table | 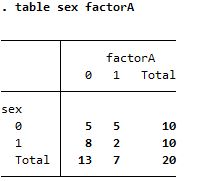
|
Both creates the same table but tabulate is better visualized |
|---|---|---|
| tabulate | 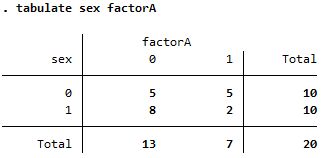
| |
| tabstat | 
|
Both reports mean but summarize is more detailed; needs bysort option before the command |
| summarize | 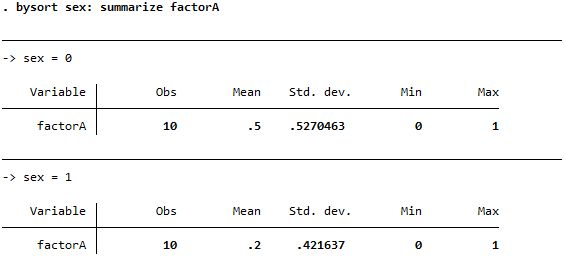
|
Summary of sex based on factorA
| table | 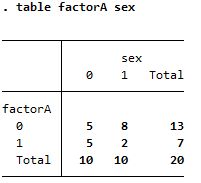
|
Both creates the same table but tabulate is better visualized |
|---|---|---|
| tabulate | 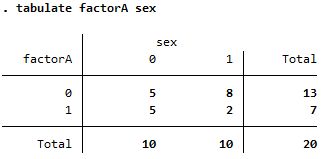
| |
| tabstat | 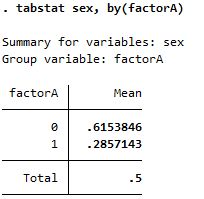
|
Both reports mean but summarize is more detailed; needs bysort option before the command |
| summarize | 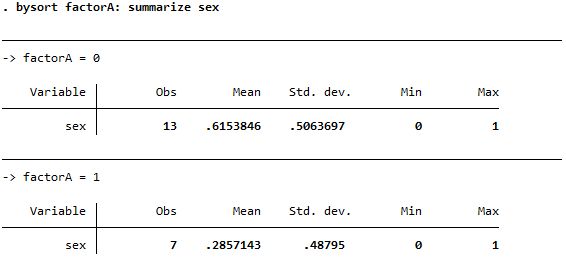
|
Summary of data1 based on disease
| table | *Both do not create a meaningful table for continuous variable | |
|---|---|---|
| tabulate | ||
| tabstat | 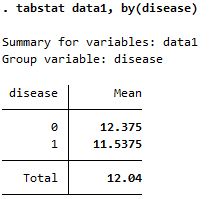
|
Both reports mean but summarize is more detailed; needs bysort option before the command |
| summarize | 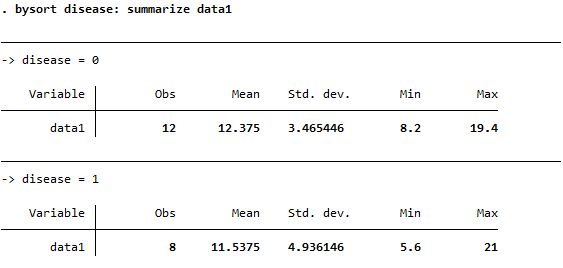
| |