「Keys for Tropical Medicine 1」の版間の差分
ナビゲーションに移動
検索に移動
Vaccipedia.admin (トーク | 投稿記録) |
Vaccipedia.admin (トーク | 投稿記録) |
||
| 306行目: | 306行目: | ||
==Protozoa== | ==Protozoa== | ||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''How protozoa differ from bacteria''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''Classification of major protozoa in terms of reproduction manners and infecting organs/cells''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
-> [[Overview_of_protozoa]] | -> [[Overview_of_protozoa]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''Essential knowledge of malaria''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | *Epidemiology and disease burden of malaria worldwide | ||
| + | **Especially of ''Plasmodium falciparum'' | ||
| + | *Essential lifecycle | ||
| + | #Mosquito stage | ||
| + | #Human liver stage | ||
| + | #Human red cell stage | ||
| + | *Only ''P. vivax'' and ''P. ovale'' have hypnotic stage in liver cause '''relapse''' | ||
| + | **All species cause '''recrudescence''' due to inadequate/improper treatment | ||
| + | *Fever, Anemia, Splenomegaly | ||
| + | *Cerebral malaria almost only by ''P. falciparum'', which leads to high mortality | ||
| + | *Diagnosis made by Rapid Diagnostic Test (RDT) and Blood smear microscopy (Giemsa staining) | ||
| + | **Blood smear includes thick smear (just to detect ''Plasmodium'') and thin smear (confirm species of ''Plasmodium'' and degree of parasitemia as disease severity) | ||
2022年12月5日 (月) 22:55時点における版
Overview of Tropical Medicine
Definition of the tropics
- Between the Tropic of Cancer (north latitude 23°26′) and the Tropic of Capricorn (south latitude 23°26′)
- Covers 40% of land surfaces and 40% of population
Top 3 causes of death in LMICs, HICs and worldwide in 2016
*Bold names are communicable diseases
| Worldwide | LMICs | HICs |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Changes of top 10 causes of death worldwide from 2010 to 2016
- Tuberculosis ranked down to the 10th in 2016 from the 6th in 2010
- HIV/AIDS ranked down out of 10 in 2016 from the 7th in 2010
List Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) and what are not listed as NTDs
| Virus |
|
|---|---|
| Bacteria |
|
| Protozoa |
|
| Parasites - Nematodes |
|
| Parasites - Trematodes |
|
| Parasites - Cestodes |
|
| Ectoarasites |
|
| Fungi |
|
| Non-communicable |
|
- These are NOT listed as NTDs
- HIV/AIDS
- Tuberculosis
- Malaria
- Lower respiratory infections
- Diarrhea
Bacteria
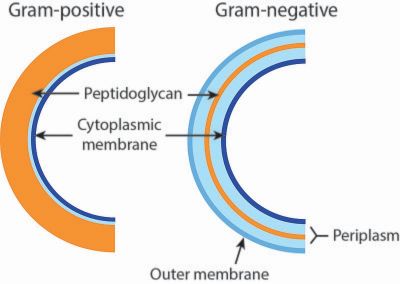
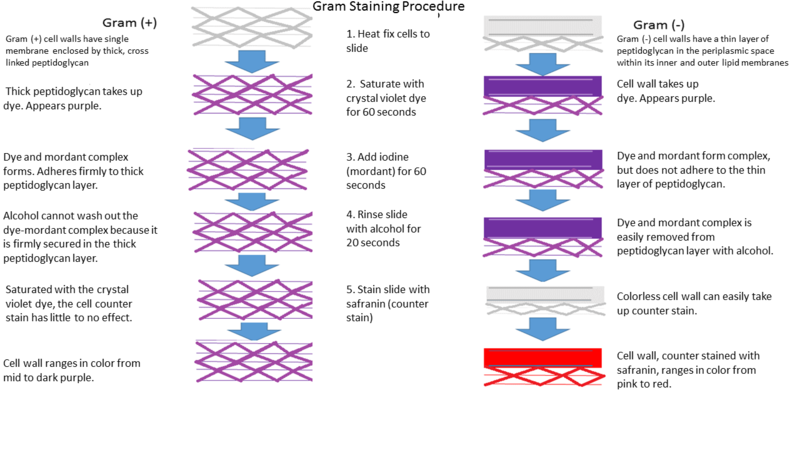
Biological basis of Gram staining
- Bacteria have both of cell wall and cell membrane
- Human and other animal cells have no cell wall
- Plant cells have cell wall
- Some bacteria have thick cell wall without outer membrane
- Other bacteria have thin cell wall with outer membrane
- Cell wall contains a layer of Peptidoglycan
- Thick peptidoglycan layer catches and keep crystal violet with iodine
- Outer membrane catches crystal violet with iodine but easily lose them by ethanol rinsing
Classification of major Gram-Positive cocci
| Catalase Positive in tubes |
Coagulase Positive in tubes |
Coagulase Negative in tubes |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
| Catalase Negative in tubes |
α hemolytic (partial hemolysis) on media |
β hemolytic (complete hemolysis) on media |
γ hemolytic (no hemolysis) on media |
|||
|
|
|
||||
Classification of major Gram-Positive bacilli
| Spore forming | Non-spore forming | |
|---|---|---|
| Aerobic |
|
|
| Anaerobic |
|
|
Classification of major Gram-Negative cocci
Classification of major Gram-Negative bacili
| Lactose fermenting |
|
|---|---|
| Non-lactose fermenting |
|
| Non-fermenting |
|
Protozoa
How protozoa differ from bacteria
Classification of major protozoa in terms of reproduction manners and infecting organs/cells
{{collapse |title= Essential knowledge of malaria |content=
- Epidemiology and disease burden of malaria worldwide
- Especially of Plasmodium falciparum
- Essential lifecycle
- Mosquito stage
- Human liver stage
- Human red cell stage
- Only P. vivax and P. ovale have hypnotic stage in liver cause relapse
- All species cause recrudescence due to inadequate/improper treatment
- Fever, Anemia, Splenomegaly
- Cerebral malaria almost only by P. falciparum, which leads to high mortality
- Diagnosis made by Rapid Diagnostic Test (RDT) and Blood smear microscopy (Giemsa staining)
- Blood smear includes thick smear (just to detect Plasmodium) and thin smear (confirm species of Plasmodium and degree of parasitemia as disease severity)