「Keys for Tropical Medicine 1」の版間の差分
Vaccipedia.admin (トーク | 投稿記録) |
Vaccipedia.admin (トーク | 投稿記録) |
||
| (同じ利用者による、間の15版が非表示) | |||
| 2行目: | 2行目: | ||
{{collapse | {{collapse | ||
|title= | |title= | ||
| − | Definition of the tropics | + | '''Definition of the tropics''' |
|content= | |content= | ||
*Between the Tropic of Cancer (north latitude 23°26′) and the Tropic of Capricorn (south latitude 23°26′) | *Between the Tropic of Cancer (north latitude 23°26′) and the Tropic of Capricorn (south latitude 23°26′) | ||
| 10行目: | 10行目: | ||
{{collapse | {{collapse | ||
|title= | |title= | ||
| − | Top 3 causes of death in LMICs, HICs and worldwide in 2016 | + | '''Top 3 causes of death in LMICs, HICs and worldwide in 2016''' |
|content= | |content= | ||
<nowiki>*</nowiki>'''Bold names''' are communicable diseases | <nowiki>*</nowiki>'''Bold names''' are communicable diseases | ||
| 41行目: | 41行目: | ||
{{collapse | {{collapse | ||
|title= | |title= | ||
| − | Changes of top 10 causes of death worldwide from 2010 to 2016 | + | '''Changes of top 10 causes of death worldwide from 2010 to 2016''' |
|content= | |content= | ||
*Tuberculosis ranked down to the 10th in 2016 from the 6th in 2010 | *Tuberculosis ranked down to the 10th in 2016 from the 6th in 2010 | ||
| 49行目: | 49行目: | ||
{{collapse | {{collapse | ||
|title= | |title= | ||
| − | List Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) and what are not listed as NTDs | + | '''List Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) and what are not listed as NTDs''' |
|content= | |content= | ||
*[https://www.who.int/health-topics/neglected-tropical-diseases#tab=tab_1 List of NTDs by WHO] | *[https://www.who.int/health-topics/neglected-tropical-diseases#tab=tab_1 List of NTDs by WHO] | ||
| 150行目: | 150行目: | ||
**Lower respiratory infections | **Lower respiratory infections | ||
**Diarrhea | **Diarrhea | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Virus== | ||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''Two major classification manners of viruses''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | *RNA virus vs DNA virus | ||
| + | *Enveloped virus vs Non-enveloped virus | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''Diagnostic methods of virus infection''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | *Detection of pathogen | ||
| + | **Genome detection by PCR and other NAATs (nucleic acid amplification tests) | ||
| + | **Antigen detection by ELISA and immunochromatography, etc. | ||
| + | **Virus isolation using human/animal cells | ||
| + | *Detection of antibody | ||
| + | **IgM or IgG by ELISA and immunochromatography, etc. | ||
| + | **Neutralizing antibody using human/animal cells | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''Definition of arboviruses''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''Classification of major arboviruses and their major vectors''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''Warning signs of severe dengue''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''List of Vaccine-preventable arbovirus infections''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''Essential knowledge of HIV''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | [https://drive.google.com/file/d/1N5GBSimejHLEk9We-fEC240mgjuT5-PC/view?usp=share_link Watch our Group 4 video and pick up information described in blue letters!] | ||
}} | }} | ||
| 155行目: | 208行目: | ||
{{collapse | {{collapse | ||
|title= | |title= | ||
| − | Biological basis of Gram staining | + | '''Biological basis of Gram staining''' |
|content= | |content= | ||
*Bacteria have both of '''cell wall''' and '''cell membrane''' | *Bacteria have both of '''cell wall''' and '''cell membrane''' | ||
| 163行目: | 216行目: | ||
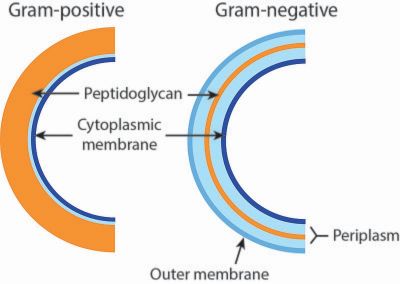
*Other bacteria have thin cell wall with outer membrane | *Other bacteria have thin cell wall with outer membrane | ||
*Cell wall contains a layer of Peptidoglycan | *Cell wall contains a layer of Peptidoglycan | ||
| − | [[File:File_Bacterial_cell_walls.jpg|none]] | + | [[File:File_Bacterial_cell_walls.jpg|none|400px]] |
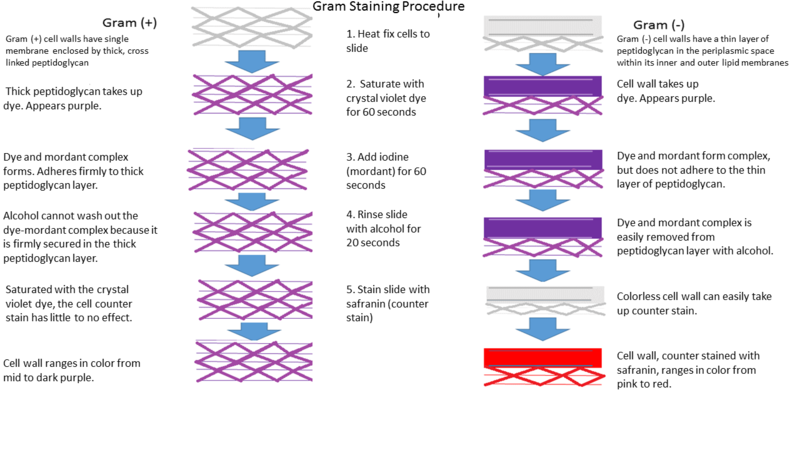
*Thick peptidoglycan layer catches and keep crystal violet with iodine | *Thick peptidoglycan layer catches and keep crystal violet with iodine | ||
*Outer membrane catches crystal violet with iodine but easily lose them by ethanol rinsing | *Outer membrane catches crystal violet with iodine but easily lose them by ethanol rinsing | ||
[[File:Gram_Stain.png|none|800px]] | [[File:Gram_Stain.png|none|800px]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''Classification of major Gram-Positive cocci''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | <table border="1" style="border-collapse:collapse"> | ||
| + | <tr bgcolor="lightgray"> | ||
| + | <th rowspan="2" bgcolor="lightgray">Catalase Positive<br>in tubes</th> | ||
| + | <th colspan="3">Coagulase Positive<br>in tubes</th> | ||
| + | <th colspan="3">Coagulase Negative<br>in tubes</th> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td colspan="3"> | ||
| + | *''Staphylococcus aureus'' | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td colspan="3"> | ||
| + | *''Staphylococcus epidermidis'' | ||
| + | *''Staphylococcus saprophyticus'' | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr bgcolor="lightgray"> | ||
| + | <th rowspan="2" bgcolor="lightgray">Catalase Negative<br>in tubes</th> | ||
| + | <th colspan="2">α hemolytic<br>(partial hemolysis)<br>on media</th> | ||
| + | <th colspan="2">β hemolytic<br>(complete hemolysis)<br>on media</th> | ||
| + | <th colspan="2">γ hemolytic<br>(no hemolysis)<br>on media</th> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td colspan="2"> | ||
| + | *''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' | ||
| + | *''Streptococcus suis'' | ||
| + | *viridans ''Streptococcus'' | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td colspan="2"> | ||
| + | *Group A (beta) streptococci (''Streptococcus pyogenes'') | ||
| + | *Group B (beta) streptococci (''Streptococcus agalactae'') | ||
| + | *Group C (beta) streptococci | ||
| + | *Group G (beta) streptococci | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td colspan="2"> | ||
| + | *''Streptococcus bovis'' | ||
| + | *''Enterococcus faecium'' | ||
| + | *''Enterococcus faecalis'' | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''Classification of major Gram-Positive bacilli''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | <table border="1" style="border-collapse:collapse"> | ||
| + | <tr bgcolor="lightgray"> | ||
| + | <th></th> | ||
| + | <th>Spore forming</th> | ||
| + | <th>Non-spore forming</th> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th bgcolor="lightgray">Aerobic</th> | ||
| + | <td> | ||
| + | *''Bacillus anthracis'' | ||
| + | *''Bacillus cereus'' | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td> | ||
| + | *''Corynebacterium diphtheria'' | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th bgcolor="lightgray">Anaerobic</th> | ||
| + | <td> | ||
| + | *''Clostridium tetani'' | ||
| + | *''Clostridium perfringens'' | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td> | ||
| + | *''Listeria monocytogenes'' | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''Classification of major Gram-Negative cocci''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | <table border="1" style="border-collapse:collapse"> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''Classification of major Gram-Negative bacili''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | <table border="1" style="border-collapse:collapse"> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th bgcolor="lightgray">Lactose fermenting</th> | ||
| + | <td> | ||
| + | *''Escherichia coli'' | ||
| + | *''Klebsiella pneumoniae'' | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th bgcolor="lightgray">Non-lactose fermenting</th> | ||
| + | <td> | ||
| + | *''Shigella'' spp. | ||
| + | *''Salmonella'' spp. | ||
| + | *''Yersinia pestis'' | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th bgcolor="lightgray">Non-fermenting</th> | ||
| + | <td> | ||
| + | *''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' | ||
| + | *''Burkholderia pseudomallei'' | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''Essential knowledge of Tuberculosis''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | *Bacterial structure different from other major bacteria | ||
| + | **Too thick lipid-rich cell wall; acid fast | ||
| + | *Epidemiology and disease burden | ||
| + | *Three species causing clinical tuberculosis | ||
| + | **''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' | ||
| + | **''M. bovis'' | ||
| + | **''M. africanum'' (only in Africa) | ||
| + | *Airborne transmission | ||
| + | **No contact/fomite transmission | ||
| + | **Contaminated milk ingestion may cause food-borne tuberculosis by ''M. bovis'' (''bovis'' means cow) | ||
| + | *Three major Symptoms | ||
| + | **Cough for weeks | ||
| + | **Weight loss for weeks | ||
| + | **Night sweats for weeks | ||
| + | *Diagnostic methods | ||
| + | **sputum microscopy (Ziel-Nielsen staining) | ||
| + | **genome detection by GeneXpert (also detects resistance) | ||
| + | **culture (6-8 weeks) | ||
| + | **chest X-ray | ||
| + | **urine LAM assay | ||
| + | **Mantoux test and IGRA for latent infection | ||
| + | *Potential of long-term (months, years to decades) infection | ||
| + | **Human immune system cannot eliminate established infection but only contains (just to 'hide' ''Mycobacterium'') | ||
| + | *HIV-Tb co-infection is soooooo major public health problem | ||
| + | *Treatment | ||
| + | **6 months (2 intensive + 4 maintenance) | ||
| + | *Definition of drug resistance | ||
| + | **MDR | ||
| + | **XDR | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Protozoa== | ||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''How protozoa differ from bacteria''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''Classification of major protozoa in terms of reproduction manners and infecting organs/cells''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | -> [[Overview_of_protozoa]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''Essential knowledge of malaria''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | *Epidemiology and disease burden of malaria worldwide | ||
| + | **Especially of ''Plasmodium falciparum'' | ||
| + | *Essential lifecycle | ||
| + | #Mosquito stage | ||
| + | #Human liver stage | ||
| + | #Human red cell stage | ||
| + | *Only ''P. vivax'' and ''P. ovale'' have hypnotic stage in liver cause '''relapse''' | ||
| + | **All species cause '''recrudescence''' due to inadequate/improper treatment | ||
| + | *Fever, Anemia, Splenomegaly | ||
| + | *Cerebral malaria almost only by ''P. falciparum'', which leads to high mortality | ||
| + | *Diagnosis made by Rapid Diagnostic Test (RDT) and Blood smear microscopy (Giemsa staining) | ||
| + | **Blood smear includes thick smear (just to detect ''Plasmodium'') and thin smear (confirm species of ''Plasmodium'' and degree of parasitemia as disease severity) | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Parasite== | ||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''Major classification of parasites''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | *Helminth | ||
| + | **Nematode (round worm) | ||
| + | **Trematode (fluke, distoma) | ||
| + | **Cestode (tape worm) | ||
| + | *Ectoparasite | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Zoonosis== | ||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''Definition of Zoonosis''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse | ||
| + | |title= | ||
| + | '''List of major zoonoses and their host animals''' | ||
| + | |content= | ||
| + | <table border="1" style="border-collapse:collapse"> | ||
| + | <tr bgcolor="lightgray"> | ||
| + | <th></th> | ||
| + | <th>Disease</th> | ||
| + | <th>Pathogen</th> | ||
| + | <th>Host animals</th> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th rowspan="4" bgcolor="lightgray">Virus</th> | ||
| + | <td>Ebola virus disease</td> | ||
| + | <td>Ebolavirus</td> | ||
| + | <td>Fruit bat</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Marburg disease</td> | ||
| + | <td>Marburg virus</td> | ||
| + | <td>Fruit bat</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)</td> | ||
| + | <td>MERS coronavirus</td> | ||
| + | <td>Camel <- Bat?</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (SFTS)</td> | ||
| + | <td>SFTS virus</td> | ||
| + | <td>Deer, wild bores</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th bgcolor="lightgray">Bacteria</th> | ||
| + | <td>Anthrax</th> | ||
| + | <td>''Bacillus anthracis''</td> | ||
| + | <td>Herbivore (cattle, sheep, goat) | ||
| + | </table> | ||
}} | }} | ||
2022年12月5日 (月) 23:45時点における最新版
Overview of Tropical Medicine
Definition of the tropics
- Between the Tropic of Cancer (north latitude 23°26′) and the Tropic of Capricorn (south latitude 23°26′)
- Covers 40% of land surfaces and 40% of population
Top 3 causes of death in LMICs, HICs and worldwide in 2016
*Bold names are communicable diseases
| Worldwide | LMICs | HICs |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Changes of top 10 causes of death worldwide from 2010 to 2016
- Tuberculosis ranked down to the 10th in 2016 from the 6th in 2010
- HIV/AIDS ranked down out of 10 in 2016 from the 7th in 2010
List Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) and what are not listed as NTDs
| Virus |
|
|---|---|
| Bacteria |
|
| Protozoa |
|
| Parasites - Nematodes |
|
| Parasites - Trematodes |
|
| Parasites - Cestodes |
|
| Ectoarasites |
|
| Fungi |
|
| Non-communicable |
|
- These are NOT listed as NTDs
- HIV/AIDS
- Tuberculosis
- Malaria
- Lower respiratory infections
- Diarrhea
Virus
Two major classification manners of viruses
- RNA virus vs DNA virus
- Enveloped virus vs Non-enveloped virus
Diagnostic methods of virus infection
- Detection of pathogen
- Genome detection by PCR and other NAATs (nucleic acid amplification tests)
- Antigen detection by ELISA and immunochromatography, etc.
- Virus isolation using human/animal cells
- Detection of antibody
- IgM or IgG by ELISA and immunochromatography, etc.
- Neutralizing antibody using human/animal cells
Definition of arboviruses
Classification of major arboviruses and their major vectors
Warning signs of severe dengue
List of Vaccine-preventable arbovirus infections
Essential knowledge of HIV
Bacteria
Biological basis of Gram staining
- Bacteria have both of cell wall and cell membrane
- Human and other animal cells have no cell wall
- Plant cells have cell wall
- Some bacteria have thick cell wall without outer membrane
- Other bacteria have thin cell wall with outer membrane
- Cell wall contains a layer of Peptidoglycan
- Thick peptidoglycan layer catches and keep crystal violet with iodine
- Outer membrane catches crystal violet with iodine but easily lose them by ethanol rinsing
Classification of major Gram-Positive cocci
| Catalase Positive in tubes |
Coagulase Positive in tubes |
Coagulase Negative in tubes |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
| Catalase Negative in tubes |
α hemolytic (partial hemolysis) on media |
β hemolytic (complete hemolysis) on media |
γ hemolytic (no hemolysis) on media |
|||
|
|
|
||||
Classification of major Gram-Positive bacilli
| Spore forming | Non-spore forming | |
|---|---|---|
| Aerobic |
|
|
| Anaerobic |
|
|
Classification of major Gram-Negative cocci
Classification of major Gram-Negative bacili
| Lactose fermenting |
|
|---|---|
| Non-lactose fermenting |
|
| Non-fermenting |
|
Essential knowledge of Tuberculosis
- Bacterial structure different from other major bacteria
- Too thick lipid-rich cell wall; acid fast
- Epidemiology and disease burden
- Three species causing clinical tuberculosis
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- M. bovis
- M. africanum (only in Africa)
- Airborne transmission
- No contact/fomite transmission
- Contaminated milk ingestion may cause food-borne tuberculosis by M. bovis (bovis means cow)
- Three major Symptoms
- Cough for weeks
- Weight loss for weeks
- Night sweats for weeks
- Diagnostic methods
- sputum microscopy (Ziel-Nielsen staining)
- genome detection by GeneXpert (also detects resistance)
- culture (6-8 weeks)
- chest X-ray
- urine LAM assay
- Mantoux test and IGRA for latent infection
- Potential of long-term (months, years to decades) infection
- Human immune system cannot eliminate established infection but only contains (just to 'hide' Mycobacterium)
- HIV-Tb co-infection is soooooo major public health problem
- Treatment
- 6 months (2 intensive + 4 maintenance)
- Definition of drug resistance
- MDR
- XDR
Protozoa
How protozoa differ from bacteria
Classification of major protozoa in terms of reproduction manners and infecting organs/cells
Essential knowledge of malaria
- Epidemiology and disease burden of malaria worldwide
- Especially of Plasmodium falciparum
- Essential lifecycle
- Mosquito stage
- Human liver stage
- Human red cell stage
- Only P. vivax and P. ovale have hypnotic stage in liver cause relapse
- All species cause recrudescence due to inadequate/improper treatment
- Fever, Anemia, Splenomegaly
- Cerebral malaria almost only by P. falciparum, which leads to high mortality
- Diagnosis made by Rapid Diagnostic Test (RDT) and Blood smear microscopy (Giemsa staining)
- Blood smear includes thick smear (just to detect Plasmodium) and thin smear (confirm species of Plasmodium and degree of parasitemia as disease severity)
Parasite
Major classification of parasites
- Helminth
- Nematode (round worm)
- Trematode (fluke, distoma)
- Cestode (tape worm)
- Ectoparasite
Zoonosis
Definition of Zoonosis
List of major zoonoses and their host animals
| Disease | Pathogen | Host animals | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virus | Ebola virus disease | Ebolavirus | Fruit bat |
| Marburg disease | Marburg virus | Fruit bat | |
| Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) | MERS coronavirus | Camel <- Bat? | |
| Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (SFTS) | SFTS virus | Deer, wild bores | |
| Bacteria | Anthrax | Bacillus anthracis | Herbivore (cattle, sheep, goat) |