提供: Vaccipedia | Resources for Vaccines, Tropical medicine and Travel medicine
ナビゲーションに移動
検索に移動
| Navigation Menu
|

|
| General issues of Vaccine
|
|
|
| General issues of Tropical med.
|
|
|
| General issues of Travel med.
|
|
|
| Trematode (fluke, distoma)
|
|
|
schistosoma is distinct from other trematoda
- trematode中schistosomaは他のtrematodeと異なる特徴を持つ
| schistosoma |
other trematode
|
transmitted to human
by percutaneous invasion of cercariae |
transmitted to human
by oral ingestion of metacercariae
|
| male and female separated 雌雄別体 |
hermaphrodite雌雄同体
|
does not require 2nd intermediate host
(no metacercariae stage) |
requires 2nd intermediate host
|
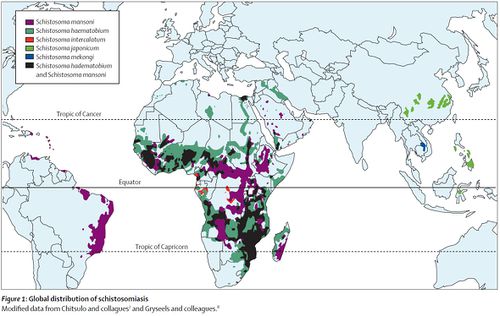
distribution
lifecycle
| Intermediate host
|
| Category
|
snails
|
| Latin
|
Oncomelania nosophora 宮入貝 in Japan
|
| Inward infection
|
- eggs hatch in freshwater to miracidia
- miracidia invade snail tissue
|
| Organ
|
snail tissue
|
| Reproduction
|
asexual
|
| Course
|
- miracidia grow into sporocysts in snail tissue
- sporocysts release cercariae in snail tissue
|
| Detection
|
|
| Outward transmission
|
cercariae swim into freshwater in reaction to light (sunlight)
|
| Definitive host
|
| Category
|
human being
|
| Latin
|
|
| Inward infection
|
- cercariae penetrate skin of human who put body into contaminated freshwater
- cercariae lose their tail during skin penetration and become schistosomulae
- schistosomulae enter into circulation and migrate to specific organ to grow up to adults
|
| Organ
|
- venous plexus of urinary bladder in case of S. haematobium
- portal vein through liver in case of other spp.
|
| Reproduction
|
sexual (different from other trematodes)
|
| Course
|
- adults differentiate to male and female
- both mate in portal vein and live veins of the organ for decades
- mated female produce egg inside veins
- eggs obstruct veins and induce inflammatory reaction to cause disease
|
| Detection
|
- microscopic detection of eggs in urine (S. haematobium) or feces (other spp.)
- Kato-Katz technique for feces
- serological detection of protein of eggshell
- circumoval precipitin test (COPT)
|
| Outward transmission
|
- eggs are released into freshwater from urine or feces
- eggs hatch in freshwater and invade snail tissue
|
Schistosoma japonicum
- Katsurada Fujiro found 26 May 1904 from a cat in Yamanashi(水腫腸満)
- Fujinami Kan found 30 May 1904 from a murder victim in Katayama, Hiroshima(片山病)
- found egg in 1904 in Saga(奇病)
pathogenesis
- adult female paired by male migrate to messenteric vein from portal vein and lay eggs into messenteric venule, which are secreted from messenteric venule to intestinal lumen
- eggs also reach urinary bladder or genital tract and generate inflammation, followed by necrosis of tissue and perforation to intestine, resulted in extracorporeal distribution of egg via stool
- eggs are also distributed in liver and cause inflammation resulting in cirrhosis
- inflammation is exclusively due to egg
- adult pairs do not cause disease per se
co-infection
- HIV
- Typhoid
- Salmonella typhi has crossover antigenicity with Schistosoma and makes immune-tolerance against Schistosoma infection
- Also Salmonella hide between male and female schistosomes in the gynecophoric canal
- HepB/C
treatment
- praziquantel was discovered only in mid-1970s in Germany
- praziquantel only kills adult schistosoma
control
- In Japanese history before introduction of praziquantel, one of ways to control was eliminate intermediate hosts, snails - Oncomelania nosophora 宮入貝
- After introduction of praziquantel
- Malacological monitoring of snails in endemic area
- Improve water irrigation in order to avoid colonization of snails
- Effective screening of people in endemic area to detect actively infected patients
- Periodical mass drug administration to people in endemic area
- Praziquantel 30mg/kg twice for MDA
- Praziquantel 60mg/kg in two divided dose for detected patients
