「Meningococcus」の版間の差分
ナビゲーションに移動
検索に移動
Vaccipedia.admin (トーク | 投稿記録) |
Vaccipedia.admin (トーク | 投稿記録) |
||
| 49行目: | 49行目: | ||
===current vaccines=== | ===current vaccines=== | ||
| − | * | + | *A polysaccharide |
| − | *A,C,Y,W135 | + | **MenAfriVac |
| + | *C conjugate | ||
| + | *A,C,Y,W135 conjugate | ||
| + | **Menactra (Sanofi Pasteur) | ||
| + | **Menveo (GSK) | ||
| + | **Nimenrix (Pfizer) | ||
| + | *B polysaccharide | ||
| + | **Bexsero (GSK) | ||
| + | **Trumenba (Pfizer) | ||
| + | **VA-MENGOC-BC (Finlay Institute of Cuba) | ||
===issues of men B vaccine=== | ===issues of men B vaccine=== | ||
2021年6月1日 (火) 11:37時点における版
| Navigation Menu |
| General issues of Vaccine | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| General issues of Travel med. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Immunology | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Epi & Stats | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Virus | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| COVID-19 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Bacteria | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Rickettsia | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Protozoa | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Fungi | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Nematode (roundworm) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Trematode (fluke, distoma) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Cestode (tapeworm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Medical Zoology | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
目次
pathogen
- Neisseria meningitidis
- gram negative diplococci
- carriage in nasopharynx
- 12 identified capsular serogroups
- common pathogenic serogroup A, B, C, W, X, Y
- seasonal epidemics by group A, C
- meningitis belt
- sporadic cases by e.g. group B
- Latin America
- Norway
- New Zealand
- immunity generated by polysaccharide capsule except B
- may be the reason that herd immunity development relatively slow and sporadic outbreaks continue in above countries
epidemiology
- highest < 2 y/o and adolescent
- annual outbreak during dry season in meningitis belt
- dry winds make people's nose drier resulting in easy
- wide range difference of nasopharynx carriage between countries
- reason totally unknown
- NZ & 3%
- Nigeria boarding house 30-40%
transmission
- aerosol
- fomite
- adolescent activity
clinical picture
- fever
- distinctive petechiae anywhere in whole body
- no fading by pressure with glass tumbler - "tumbler test"
- resulting in purple bruising of skin
- photophobia
- headache, neck stiffness, vomiting
- irritability and/or confusion
vaccine
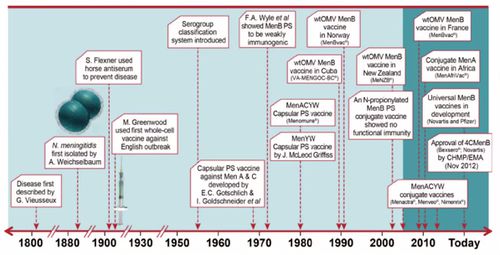
development history
- 1960s - purified PS vaccines for A and C
- immunity short term due to lack of T-cell involvement
- 1990s - conjugated vaccines for A and C after success of Hib conjugate vaccine
- 2000s - monovalent A vaccine for Africa
- "MenAfriVac"
current vaccines
- A polysaccharide
- MenAfriVac
- C conjugate
- A,C,Y,W135 conjugate
- Menactra (Sanofi Pasteur)
- Menveo (GSK)
- Nimenrix (Pfizer)
- B polysaccharide
- Bexsero (GSK)
- Trumenba (Pfizer)
- VA-MENGOC-BC (Finlay Institute of Cuba)
issues of men B vaccine
- polysaccharide of B is relatively low immunogenic
- the reason
- polysaccharide of B has potential toxicity for infant brain
- PS of B shows interaction with fatal brain cells which suggests potential of causing neurological damage for young infants